Understanding NIST Incident Response Plan Steps in Detail
In the ‘Computer Security Incident Handling Guide,’ or SP 800-61 Rev. 2, the National Institute of Standards and Technology, usually referred to as NIST, provides its guidelines on Cybersecurity Incident Management and Response. Since the framework can be complicated to grasp, DoD companies can hire experts for CMMC solution and services.
NIST Incident Response Strategy
Given the increasing complexity and frequency of cyber assaults, malware infections, and security breaches throughout the world, computer security incident management has become a key corporate activity. It has now become essential to approach IT and data security from the standpoint of reaction instead of prevention.
The NIST’s Cybersecurity Incident Handling Guide aims to help organizations improve their overall security and incident management abilities via proper planning, cybersecurity education, and allocation of resources.
It also emphasizes post-incident activities and data analysis in order to improve security procedure and offer the chance for better uncovering and reaction in the future.
In a nutshell, the guide’s overwhelming message to the entire firm will be assaulted at some point in its existence. As a result, the best method to strengthen your data security and endurance strategy is to guarantee that your cybersecurity staff is sufficiently trained, that your company recognizes cybersecurity and incident handling, and that all relevant players feel responsible.
“Creating an incident management policy and strategy” is the first need outlined in the guidance for developing an event response capability.
What exactly is a Cyber Security Incident Response Plan (CSIRP)?
A Cyber Issue Response plan is a road map for security professionals to follow when dealing with an attempt to breach cybersecurity. It provides basic guidance to the assault management staff and guides them how to promptly react following a cybersecurity occurrence.
This strategy should be tailored to the nature, scope, size, and aims of the organization. Some major criteria in this strategy, however, are consistent across sectors and regions.
Steps for the NIST Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan
Different Cyber Incident Response Plan Templates explain the phases or procedures of appropriate incident response in various ways.
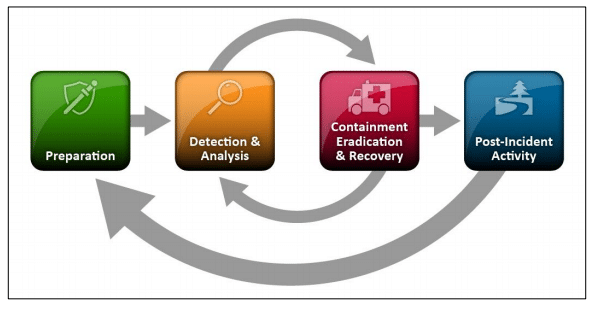
According to NIST, the primary stages of the Cybersecurity Incident Response Process are as follows:
Here is an explanation of each of the steps in the Incident Response Lifecycle.
Preparation:
As the term implies, this phase focuses on preparing the organization for a cybersecurity attack. It entails forming and educating a security incident response staff, as well as deploying technologies and assets that might prevent security problems from occurring. Even though the incident response staff is not accountable for procuring assets, prevention of events falls under the heading of preparation.
Detection and Analysis:
While no organization can be fully prepared for possible future assault, it is prudent to keep a framework in position to cope with the most prevalent attack vectors. Fulfilling CMMC compliance requirements is also essential when it comes to cybersecurity.
Another factor that contributes to the importance of the Detection stage is the fact that many firms are unable to determine whether or not they have come under the assault of cybercriminals. Because timely identification is critical, the security response team will be in a position to confirm an event promptly and then analyze its extent – what assault approach was implemented and what resources were compromised.
Post-Incident Activity:
This phase focuses on the cyber incident’s lessons learnt. Following a large event, the NIST guideline proposes conducting a ‘lessons learned’ conference with crucial personnel on how the organization may jointly improve to be better at addressing such situations in the near future.
Proper post-event activities can give light on crucial questions surrounding an occurrence, such as what occurred and how successfully the employees handled the situation. You can also discuss the organization’s incident response plan and its efficacy in these sessions.